In the dynamic landscape of online business, entrepreneurs are constantly seeking innovative ways to monetize their websites. Affiliate marketing has emerged as a powerful strategy for both businesses and individuals to generate revenue. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of affiliate marketing, unraveling its core concepts and providing practical insights on how to get started in this lucrative domain.Affiliate marketing is the process by which a partner company earns a commission to sell someone else’s or the company’s products. The agent simply looks for the product he enjoys, and then he promotes that product and earns a fraction of the sales for each product they make. Sales are tracked through links managed from one website to another.
Table of Contents
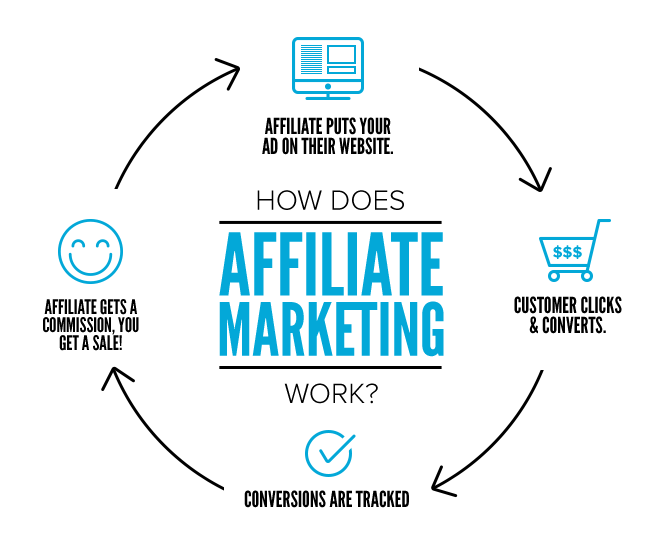
How Does Affiliate Marketing Work?
Affiliate marketing operates on a simple yet effective model involving three primary parties:
1. Seller and Product Creators:
- These are businesses or individuals who own products or services.
- They leverage affiliates to expand their reach and increase sales.
2. Agent or Publisher (Affiliate):
- Affiliates act as intermediaries who promote the seller’s products.
- They earn a commission for every sale, lead, or click generated through their marketing efforts.
3. Buyer:
- The end consumer purchasing the product or service through the affiliate’s marketing channel.
- The buyer doesn’t pay anything extra, as the affiliate commission comes from the seller’s side.
Key Points:
- Affiliates use unique tracking links to monitor their marketing performance.
- Cookies play a crucial role in attributing sales or leads to the respective affiliates.
How Are Affiliated Advertisers Paid?
Affiliated advertisers compensate their affiliates through various payment models:
1. Pay for Each Sale (Pay-per-Sale):
- Affiliates receive a commission for each sale generated through their affiliate link.
- This model motivates affiliates to focus on driving high-quality traffic that converts into actual sales.
2. Pay Per Lead (PPL):
- Advertisers pay affiliates for each lead or customer acquisition resulting from the affiliate’s marketing efforts.
- Common in industries where direct sales may not be the primary objective.
3. Pay Per Click (PPC):
- Affiliates earn a commission based on the number of clicks on their affiliate link, regardless of whether a sale occurs.
- Effective for driving traffic, particularly in niches where engagement is valuable.
Key Points:
- The payment model is typically agreed upon by the merchant and the affiliate when joining an affiliate program.
- Understanding the target audience and aligning with the right payment model is crucial for affiliate success.
Common Types of Integrated Marketing Channels
1. Influencers:
- Influencers leverage their social media presence to promote products to their engaged audience.
- Platforms like Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok are popular for influencer marketing.
2. Bloggers:
- Bloggers create content around specific niches and incorporate affiliate links within their articles.
- Blogs serve as a platform for in-depth product reviews and recommendations.
3. Paid Search with Microsites:
- Some affiliates create microsites focused on specific products or niches for paid search campaigns.
- Microsites allow for targeted messaging and optimized conversion funnels.
4. Email Lists:
- Affiliates with sizable email lists promote products to their subscribers.
- Email marketing can be highly effective when building trust with the audience over time.
5. Major Media Websites:
- Large media websites incorporate affiliate marketing into their revenue model.
- This can include news sites, review platforms, and industry-specific publications.
Key Points:
- Diversifying marketing channels mitigates risk and increases the reach of affiliate campaigns.
- Each channel requires a tailored approach to resonate with its specific audience.
How to Get Started with Affiliate Marketing
1. Build Relationships:
- Establish strong relationships with affiliate managers and fellow affiliates.
- Networking can lead to exclusive opportunities and insights.
2. Make It Your Own:
- Infuse your personality into your marketing efforts.
- Authenticity builds trust, enhancing the likelihood of conversions.
3. Start Reviewing Products and Services:
- Create detailed and unbiased reviews of products relevant to your niche.
- Reviews offer valuable information to your audience and can drive affiliate sales.
4. Use Several Sources:
- Diversify your traffic sources to avoid reliance on a single platform.
- This reduces vulnerability to algorithm changes or policy updates.
5. Choose Campaigns Carefully:
- Select affiliate programs aligned with your audience and niche.
- Quality products and reputable merchants enhance your credibility.
6. Stay Informed About Trends:
- The affiliate marketing landscape evolves, with new trends and technologies emerging.
- Regularly educate yourself to adapt and capitalize on industry developments.
Key Points:
- Success in affiliate marketing requires a combination of strategy, persistence, and adaptability.
- Continuous learning and optimization are integral to long-term success.
In conclusion, affiliate marketing is a dynamic and rewarding avenue for those willing to invest time and effort. By understanding the nuances of the industry, selecting the right affiliate programs, and employing diverse marketing channels, individuals can create sustainable revenue streams while providing value to their audience. Aspiring affiliates should embrace the learning curve, staying informed about industry trends to stay ahead in this ever-evolving field.